
 Frolicking Horses
Frolicking Horses The Horse
The Horse Feeding the horse
Feeding the horse Comfort
Comfort horse
horse Man riding horse
Man riding horse Man leading a horse
Man leading a horse Man and horse outside a house
Man and horse outside a house Going through the gate
Going through the gate Trotting across a field
Trotting across a field Feeding time
Feeding time Horse and Dog
Horse and Dog Two children riding ponies on the beach
Two children riding ponies on the beach Two horses
Two horses Two horses looking at their food
Two horses looking at their food Horse and chickens
Horse and chickens A horse
A horse Boy and Girl feeding a horse
Boy and Girl feeding a horse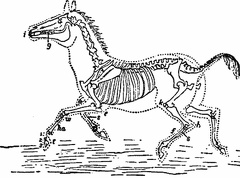 Skeleton of Horse
Skeleton of Horse Horse
Horse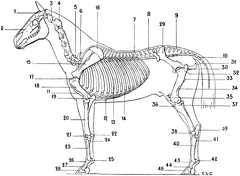 Skeleton of the Horse
Skeleton of the Horse A new method of carrying dogs
A new method of carrying dogs Zebra with young
Zebra with young Zebra with young
Zebra with young Terrified Horse
Terrified Horse Speckled horse
Speckled horse Soldier on horse
Soldier on horse Rodeo Rider
Rodeo Rider Prancing Horse
Prancing Horse Need real food
Need real food Man with two horses
Man with two horses Hunting with the dogs
Hunting with the dogs Horses running in snow
Horses running in snow Horses in stall
Horses in stall Horses Drinking
Horses Drinking Horse
Horse Horse
Horse Horse with feedbag
Horse with feedbag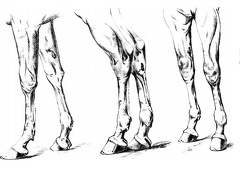 Horse legs
Horse legs Horse in stall
Horse in stall Horse Head
Horse Head Horse family
Horse family Horse drinking
Horse drinking Horse cantering
Horse cantering Horse and sheep show
Horse and sheep show Horse and Foal
Horse and Foal Horse and dogs ready for a ride
Horse and dogs ready for a ride Horse and cart with dog driver
Horse and cart with dog driver Horse affection
Horse affection Frightened Horse
Frightened Horse Feeding Time
Feeding Time Child looking after horse
Child looking after horse Bucking Horse
Bucking Horse Brown horse and foal
Brown horse and foal Blacksmith shoeing horse
Blacksmith shoeing horse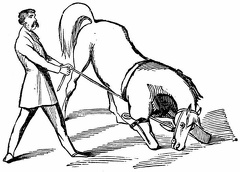 Bringing the horse to his knees
Bringing the horse to his knees Teaching the horse to back
Teaching the horse to back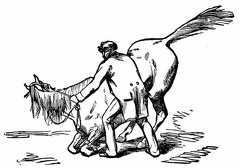 Preparing to lie down
Preparing to lie down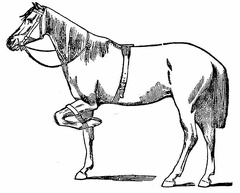 The short strap in use
The short strap in use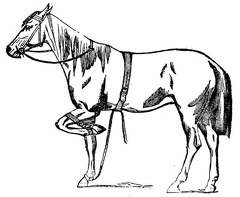 The short and the long straps
The short and the long straps



