Home / Albums / The Middle Ages 206

 The Ship Victoria
The Ship Victoria The Parish Clerk sprinkling the Knight and Lady
The Parish Clerk sprinkling the Knight and Lady The Parish Clerk sprinkling the Cook
The Parish Clerk sprinkling the Cook The Morning Stars singing together
The Morning Stars singing together The Knight-Errant’s Squire
The Knight-Errant’s Squire The Feat of Arms at St. Inglebert’s
The Feat of Arms at St. Inglebert’s The Duke of Gloucester and the Earl of Warwick
The Duke of Gloucester and the Earl of Warwick The Cat
The Cat The Canterbury Pilgrims
The Canterbury Pilgrims The Canterbury Ampulla
The Canterbury Ampulla The Beverley Minstrels
The Beverley Minstrels The Assault
The Assault Termination of the Combat
Termination of the Combat Summoning the Castle
Summoning the Castle State Carriage of the Fourteenth Century
State Carriage of the Fourteenth Century St. Paula
St. Paula St. Damasus, Hermit
St. Damasus, Hermit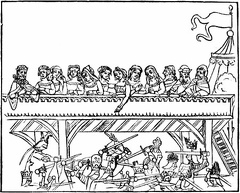 Spectators of a Tournament
Spectators of a Tournament Sir Robert Shurland
Sir Robert Shurland Sir Percival at the Reclusorium
Sir Percival at the Reclusorium Sir Launcelot and a Hermit
Sir Launcelot and a Hermit Ship of Richard Earl of Warwick
Ship of Richard Earl of Warwick Ship and Galley
Ship and Galley Shepherd with Bagpipes
Shepherd with Bagpipes Saxon Soldiers
Saxon Soldiers Saxon Soldier, in Leather Armour
Saxon Soldier, in Leather Armour Saxon Horse Soldiers
Saxon Horse Soldiers Saxon Band of Minstrels
Saxon Band of Minstrels Saint Dominic and Saint Francis
Saint Dominic and Saint Francis Rustic Merry-making
Rustic Merry-making Royal Harper
Royal Harper Royal Dinner of the time of Edward IV
Royal Dinner of the time of Edward IV Robert Braunche,of Lynn
Robert Braunche,of Lynn Regals or Organ
Regals or Organ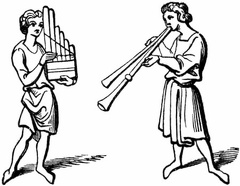 Regals and Double Pipe
Regals and Double Pipe Rectory House, West Deane, Sussex
Rectory House, West Deane, Sussex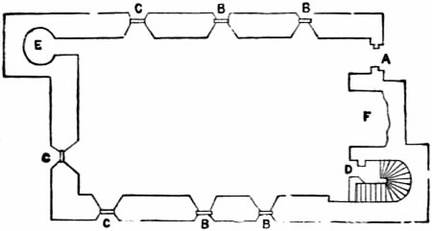 Rectory House, West Deane, Sussex - plan
Rectory House, West Deane, Sussex - plan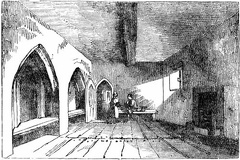 Reclusorium, or Anchorhold, at Rettenden, Essex
Reclusorium, or Anchorhold, at Rettenden, Essex Quilted Armour
Quilted Armour Saxon soldier in armour
Saxon soldier in armour Preliminaries of Combat in Green Court of Castle
Preliminaries of Combat in Green Court of Castle Preliminaries of a Combat
Preliminaries of a Combat Pope, Cardinal, and Bishop
Pope, Cardinal, and Bishop Playing at Jousting
Playing at Jousting Pilgrim
Pilgrim Pilgrim on Horseback
Pilgrim on Horseback Pilgrim Monk
Pilgrim Monk Pilgrim in Hair Shirt and Cloak
Pilgrim in Hair Shirt and Cloak Pikeman
Pikeman Passengers paying Toll
Passengers paying Toll Nun and Friar with Musical Instruments
Nun and Friar with Musical Instruments Musical Instruments of the 15th Century
Musical Instruments of the 15th Century Monumental Brass of Alderman Field and his Son, a.d. 1474
Monumental Brass of Alderman Field and his Son, a.d. 1474 Monks and Lawyers in Chapter-house
Monks and Lawyers in Chapter-house Monk in Scriptorium
Monk in Scriptorium Bringing up a youth in the middle ages
Bringing up a youth in the middle ages Men-at-Arms, Fourteenth Century
Men-at-Arms, Fourteenth Century Mediæval Dance
Mediæval Dance Marchands en Gros, Fifteenth Century
Marchands en Gros, Fifteenth Century Man-at-Arms and Archer of the Fifteenth Century
Man-at-Arms and Archer of the Fifteenth Century



